Recommended Services
Supported Scripts
Managed Email Compliance
What is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is an essential email security protocol. Let's dive into its details
Purpose and Components
DMARC builds upon existing email authentication protocols, including:
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Verifies the authenticity of the sender’s
domain by attaching a digital signature to the email. - SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Validates that the sending mail server is
authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain. - DMARC’s Goal: To prevent domain spoofing, where attackers impersonate an organization’s domain to deceive recipients.
Our Email Compliance services

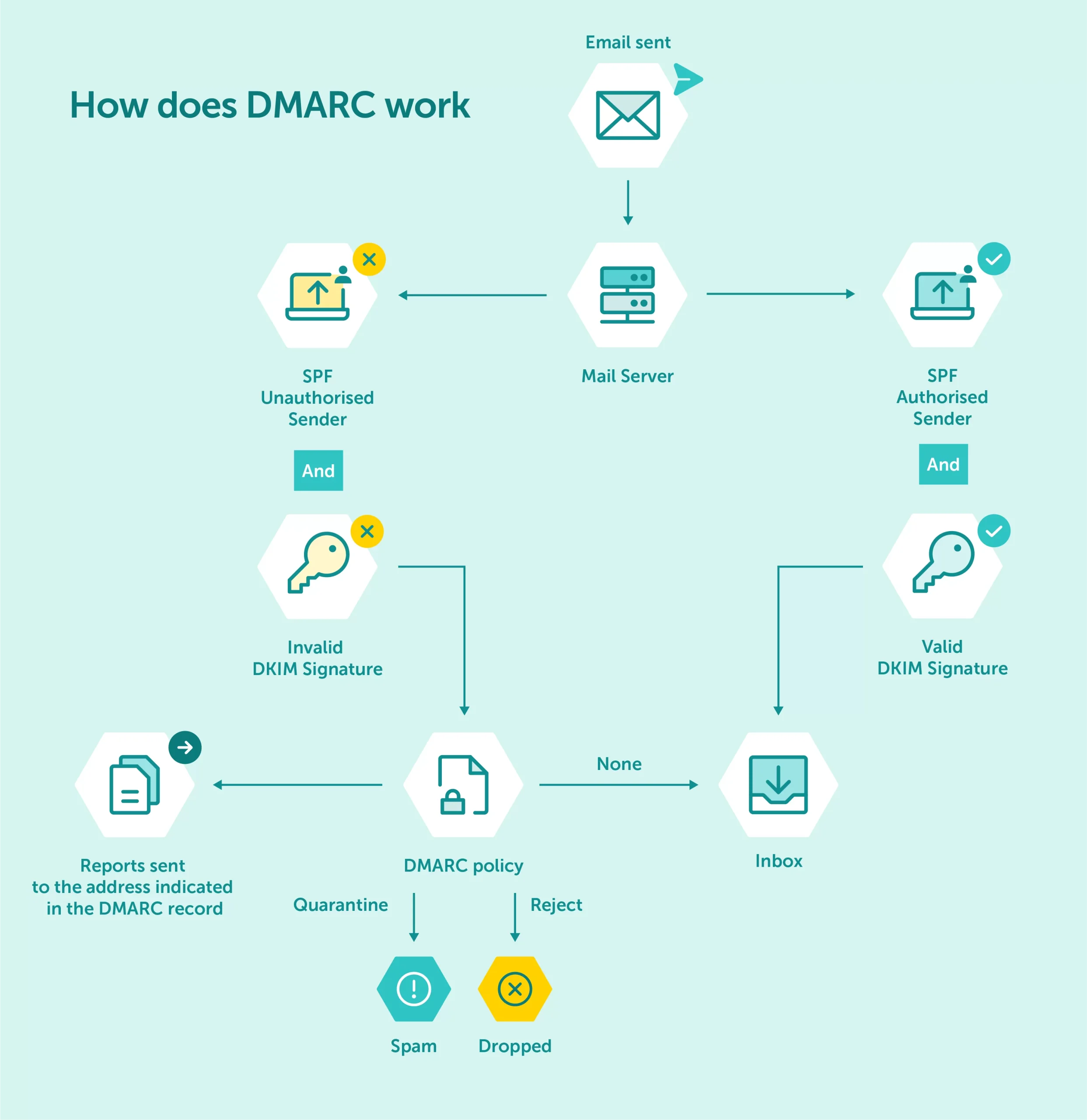
How DMARC Works
Requirements:
An email domain must have DKIM or SPF in place.
A DMARC record should be published in the DNS.
Policy Process:
After checking DKIM and SPF status, DMARC alignment ensures the email domain’s policy is shared and authenticated.
DMARC requests email servers to send XML reports to an associated email address.
These reports provide insights into email traffic using the domain.
Why Use DMARC for Email?:
- Protection: DMARC helps domain owners protect their brand by preventing unauthorized use of their domain.
- Security : It establishes consistent policies for handling unauthenticated messages, enhancing overall email security.
- Visibility: DMARC reports increase visibility into email programs, allowing domain owners to track legitimate and suspicious traffic.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
- DMARC (Domain- based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance)
- Verifies the servers allowed to send emails from a domain.
- Digitally signs emails from a domain to verify authenticity.
- Manages emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks.
- SPF records list authorized IP addresses of email servers. – Receiving mail servers check the SPF record before delivering emails.
- Domain owners sign emails with a private key. – Receiving servers verify the signature using the domain’s public key.
- DMARC policy specifies actions for failed authentication (e.g., marking as spam, delivering, or dropping). – Combines SPF and DKIM results.
- Like an employee directory confirming if an employeeworks for an organization.
- Similar to a signature on a check confirming its origin.
- Ensures proper handling when SPF or DKIM fails.
Technologies we work with






Contact Us For an Evaluation
Frequently Asked Questions FAQs
With this service you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your email domain infrastructure and dig into specific source configurations – all in the same workspace.
Yes, this service helps you to implement powerful domain-level protection against phishing, spoofing, and BEC. Automate email authentication tasks such as monitoring, alerting, and reporting.
Yes, you can gain full control over how your email domains are used worldwide, even without technical expertise. Investigate sending sources efficiently and achieve peace of mind.
Yes, you can verify and validate legitimate sending sources. Block any attempts at brand impersonation using automated and managed solutions.
Yes, Ensure your email campaigns land in recipients’ inboxes. Boost sales by delivering authentic messages that build credibility and trust.
EasyDMARC’s cloud-native approach streamlines your DMARC journey, making it accessible and effective for all IT departments. Explore their toolbox, which includes permission management, smart reporting, expert support, and real-time monitoring and alerting.

